- Measuring Growth
- Reports
- Additional Resources
- Admin Help
- General Help
Teacher Value-Added
Understanding the Report
Growth Index
The growth index is a reliable measure of whether students exceeded, met, or fell short of expected growth. This value takes into account the amount of growth the students made as well as the amount of evidence above or below expected growth. Specifically, the growth index is the growth measure divided by its standard error.
The table includes the growth index values for up to three years and the multi-year trend, when sufficient data is available. These values are plotted as color-coded diamonds in the growth index graph at the top of the report.
District Average
The option to display District Average is available when there is sufficient data. The District Average appears as a vertical purple line. This value represents the average of all teacher index values in the district for the selected grade and subject or course.
Effectiveness Levels
Each growth index is color-coded to indicate how strong the evidence is that the students exceeded, met, or fell short of expected growth.
The key at the bottom of the report provides guidance for interpreting the colors.
| Color | Growth Index Compared to Expected Growth | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Light Blue | At least 2 standard errors above | Significant evidence that the teacher's students made more growth than expected (the teacher's index is 2 or greater). |
| Green | Between 2 standard errors above and 2 standard errors below | Evidence that the students made growth as expected (the teacher's index is between -2 and 2). |
| Yellow | More than 2 standard errors below | Significant evidence that the teacher's students made less growth than expected (the teacher's index is less than -2). |
Growth Measure
Each growth measure is a conservative estimate of the academic growth the students made, on average, in a grade and subject or course. The growth measure is based on students that were linked to the teacher and the percentage of instruction. Because the growth measures are estimates, consider their associated standard errors as you interpret the values.
The growth measure is calculated differently for assessments analyzed with the gain model than it is for other assessments.
See also: Measuring Growth.
Standard Error
All growth measures on the EVAAS reports are estimates. All estimates have some amount of measurement error, which is known as the standard error. This value defines a confidence band around the growth measure, which describes how strong the evidence is that the group of students exceeded, met, or fell short of expected growth.
For more information about standard errors, see Growth Measures and Standard Errors.
Expected Growth
Expected Growth represents the point at which the students' scores, on average, align with expectations.
Expected Growth signifies the minimum amount of academic growth that educators should expect a group of students to make in a subject and grade or course. In general, this signifies appropriate, expected academic growth. Simply put, the expectation is that regardless of their entering achievement level, students served by each district, school, or teacher should at least make enough progress to maintain their achievement level relative to their peers. This is a reasonable target for educators who serve all types of students. Expected Growth is represented by a vertical green line in the graph.

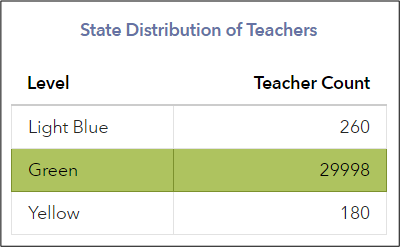
Distribution of Teachers
This distribution lists the number of teachers in each effectiveness level in the selected grade and subject or course statewide. This enables each teacher to compare their teacher value-added results with other teachers in the state for the same grade and subject or course. The distribution is only displayed for state assessments. It's important to understand that EVAAS does not fit teachers into a predetermined distribution. The number of teachers who appear in each effectiveness level is determined by the amount of statistical evidence that each teacher's group of students exceeded, met, or fell short of expected growth. The methodology does not predetermine the number or percentage of teachers whose values fall into each effectiveness level range. In fact, the relative size of each effectiveness level group varies by grade and subject or course, depending on the evidence of measurable differences in growth. |
|
Student List
To see the list of students linked to the teacher in the data, click the Student List button above the chart.
The Used in the Analysis column indicates whether each student was used in the analysis that generated the teacher's value-added report. The most common reasons that students are excluded from the analysis are:
- They don't have assessment scores
- They aren't linked to a teacher
- They don't meet membership or attendance rules
- Their scores are outliers
- They are new to the state
- They don't have enough prior assessment data
Some of these exclusion rules might not apply to all subjects. Statistical Models and Business Rules describes various conditions that can cause a student to be excluded from the analysis.
Teachers who have a Teacher Value-Added report in the selected subject, grade, or course in the most recent year have access to this report.
Showing the Growth Index or Growth Measure
The report displays the growth index graph by default. You can choose the growth measure graph from the menu below the graph. For more information about the growth measure graph, see Interpreting the Data.
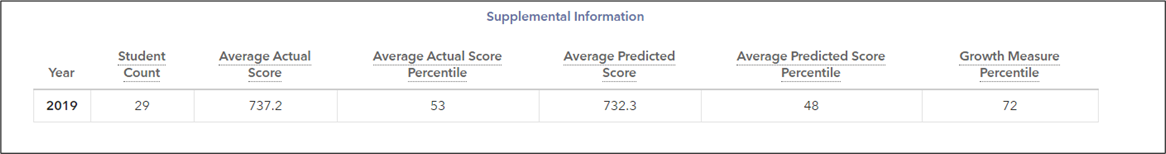
Supplemental Information Table
The table at the bottom of the report provides additional information about the students' performance and growth. This table is displayed for assessments analyzed with the predictive model.
Student Count
The number of students included in the analysis. To be included, a student must have at least three prior state assessment scores. These scores do not have to be from the same subject. Because students who lack sufficient prior data are excluded, the number of students listed here might be less than the number of students served or tested. The value in this column for the three-year average, when available, is the total number of tests across all displayed years.
For more information see Understanding the Student Count
Actual Achievement Percentile
For each year of data, the value in this column is a simple average of scores for the students included in the analysis. This value is expressed in scale score points.
Entering Achievement
An expected score is generated for each student included in the analysis. An expected score is the score the student would make on the selected assessment if the student makes average or typical growth. Entering achievement in this column is the average of the expected scores for the students included in the analysis for this teacher. Because the expected score is based on each student's prior performance, the average represents the entering achievement level for the group of students.
Entering Achievement Percentile
The entering Achievement percentile indicates where the average expected score for the group of students falls in the state distribution for this subject.